DEA Surface Reflectance (Landsat 5 TM)
DEA Surface Reflectance (Landsat 5 TM)
- Version:
- Type:
Baseline, Raster
- Resolution:
30 m
- Coverage:
16 Aug 1986 to 17 Nov 2011
- Data updates:
No further updates
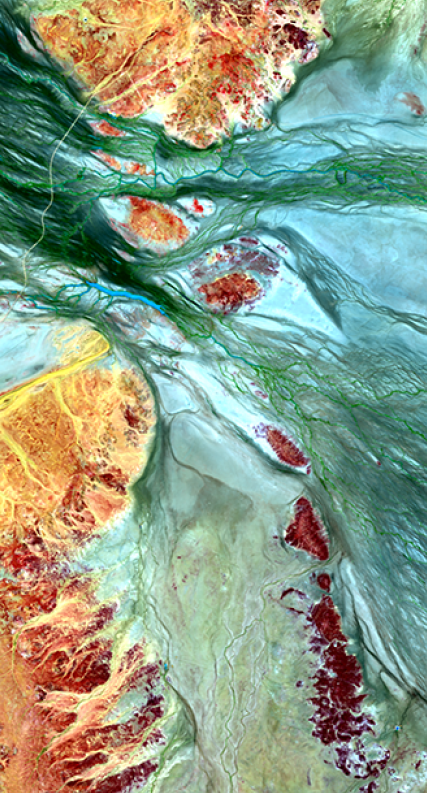
About
DEA Surface Reflectance (Landsat 5 TM) is part of a suite of Digital Earth Australia (DEA)’s Surface Reflectance datasets that represent the vast archive of images captured by the US Geological Survey (USGS) Landsat and European Space Agency (ESA) Sentinel-2 satellite programs, validated, calibrated, and adjusted for Australian conditions — ready for easy analysis.
Access the data
For help accessing the data, see the Access tab.
Key specifications
For more specifications, see the Specifications tab.
Technical name |
Geoscience Australia Landsat 5 TM Analysis Ready Data Collection 3 |
Bands |
|
Catalogue ID |
|
Collection |
|
Licence |
Cite this product
Data citation |
Fuqin, Li., Jupp, D.L.B., Sixsmith, J., Wang, L., Dorj, P., Vincent, A., Alam, I., Hooke, J., Oliver, S., Thankappan, M., 2019. GA Landsat 5 TM Analysis Ready Data Collection 3. Geoscience Australia, Canberra. https://pid.geoscience.gov.au/dataset/ga/130853
|
Publications
Li, F., Jupp, D. L. B., Reddy, S., Lymburner, L., Mueller, N., Tan, P., & Islam, A. (2010). An evaluation of the use of atmospheric and BRDF correction to standardize Landsat data. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 3(3), 257–270. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2010.2042281
Li, F., Jupp, D. L. B., Thankappan, M., Lymburner, L., Mueller, N., Lewis, A., & Held, A. (2012). A physics-based atmospheric and BRDF correction for Landsat data over mountainous terrain. Remote Sensing of Environment, 124, 756–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.06.018
Background
The United States Geological Survey’s (USGS) Landsat satellite program has been capturing images of the Australian continent for more than 30 years. This data is highly useful for land and coastal mapping studies.
In particular, the light reflected from the Earth’s surface (surface reflectance) is important for monitoring environmental resources – such as agricultural production and mining activities – over time.
We need to make accurate comparisons of imagery acquired at different times, seasons and geographic locations. However, inconsistencies can arise due to variations in atmospheric conditions, sun position, sensor view angle, surface slope and surface aspect. These need to be reduced or removed to ensure the data is consistent and can be compared over time.
What this product offers
This product takes Landsat 5 Thematic Mapper (TM) imagery captured over the Australian continent and corrects for inconsistencies across land and coastal fringes. The result is accurate and standardised surface reflectance data, which is instrumental in identifying and quantifying environmental change.
This product is a single, cohesive Analysis Ready Data (ARD) package, which allows you to analyse surface reflectance data as is, without the need to apply additional corrections.
It contains three sub-products that provide corrections or attribution information:
The resolution is a 30 m grid based on the USGS Landsat Collection 1 archive.
Applications
The development of derivative products to monitor land, inland waterways and coastal features, such as:
urban growth
coastal habitats
mining activities
agricultural activity (e.g. pastoral, irrigated cropping, rain-fed cropping)
water extent
The development of refined information products, such as:
area/units of detected surface water
area/units of deforestation
yield predictions of agricultural parcels
Compliance surveys
Emergency management
Technical information
The Thematic Mapper (TM) sensor
The TM is an advanced, multispectral scanning, Earth resources sensor which is designed to categorise the Earth’s surface. It is particularly useful for agricultural applications and identification of land use.
The Analysis Ready Data concept
The Analysis Ready Data (ARD) package allows you to get up and running with your analysis as quickly as possible with minimal data preparation and additional input. This makes it simpler for you to develop applications and for the database to execute queries.
The satellite data has been processed to a minimum set of requirements and organised into a form that allows immediate analysis and interoperability through time and with other datasets. It has been adapted from CEOS Analysis Ready Data (CARD4L).
The technical report containing the data summary for the Phase 1 DEA Surface Reflectance Validation is available.
ARD sub-products
DEA Surface Reflectance NBAR (Landsat 5 TM) This sub-product produces standardised optical surface reflectance data using robust physical models which correct for variations and inconsistencies in image radiance values. Corrections are performed using Nadir corrected Bi-directional reflectance distribution function Adjusted Reflectance (NBAR).
DEA Surface Reflectance NBART (Landsat 5 TM) This sub-product performs the same function as Surface Reflectance (Landsat 5 TM NBAR), but also applies terrain illumination correction.
The NBAR and NBART sibling products depend upon the OA product to provide accurate and reliable contextual information about the Landsat data. This ‘data provenance’ provides a chain of information which allows the data to be replicated or utilised by derivative applications. It takes a number of different forms, including satellite, solar and surface geometry and classification attribution labels.
Lineage
This product is derived from the USGS Landsat Collection 1 archive.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) MCD43A1 Version 6 Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function and Albedo (BRDF/Albedo) Model Parameters dataset was provided by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). It was produced daily using 16 days of Terra and Aqua MODIS data at 500 m resolution. See USGS: MCD43A1, NASA: MODIS BRDF / Albedo Parameter, Schaaf et al. (2002)
The ozone data was provided by Environment Canada. See Environment Canada: Global Ozone Maps
The Aerosol Optical Thickness data was provided by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO). See Qin et al. (2015)
The Precipitable Water for Entire Atmosphere data was provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) / Earth System Research Laboratory (ESRL) / Physical Sciences Division (PSD). See Kalnay et al. (1996)
The baseline Digital Surface Model (DSM) data produced from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) was provided by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA). See NGA: SRTM, NASA: SRTM
Level 1 Collection 1 data was provided by the United States Geological Survey (USGS)’s Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center. See USGS: EROS, USGS: Landsat Collection 1
Processing steps
Longitude and Latitude Calculation
Satellite and Solar Geometry Calculation
Aerosol Optical Thickness Retrieval
BRDF Shape Function Retrieval
Ozone Retrieval
Elevation Retrieval and Smoothing
Slope and Aspect Calculation
Incidence and Azimuthal Incident Angles Calculation
Exiting and Azimuthal Exiting Angles Calculation
Relative Slope Calculation
Terrain Occlusion Mask
MODTRAN
Atmospheric Correction Coefficients Calculation
Bilinear Interpolation of Atmospheric Correction Coefficients
Surface Reflectance Calculation (NBAR)
Surface Reflectance Calculation (NBAR + Terrain Illumination Correction)
Function of Mask (Fmask)
Contiguous Spectral Data Mask Calculation
Software
References
Berk, A., Conforti, P., Kennett, R., Perkins, T., Hawes, F., & van den Bosch, J. (2014, June 13). MODTRAN6: A major upgrade of the MODTRAN radiative transfer code (M. Velez-Reyes & F. A. Kruse, Eds.). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2050433
Dymond, J. R., & Shepherd, J. D. (1999). Correction of the topographic effect in remote sensing. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 37(5), 2618–2619. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.789656
Hudson, S. R., Warren, S. G., Brandt, R. E., Grenfell, T. C., & Six, D. (2006). Spectral bidirectional reflectance of Antarctic snow: Measurements and parameterization. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(D18), D18106. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007290
Kalnay, E., Kanamitsu, M., Kistler, R., Collins, W., Deaven, D., & Gandin, L. et al. (1996). The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bulletin Of The American Meteorological Society, 77(3), 437-471. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:tnyrp>2.0.co;2
Li, F., Jupp, D. L. B., Reddy, S., Lymburner, L., Mueller, N., Tan, P., & Islam, A. (2010). An evaluation of the use of atmospheric and BRDF correction to standardize Landsat data. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 3(3), 257–270. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2010.2042281
Li, F., Jupp, D. L. B., Thankappan, M., Lymburner, L., Mueller, N., Lewis, A., & Held, A. (2012). A physics-based atmospheric and BRDF correction for Landsat data over mountainous terrain. Remote Sensing of Environment, 124, 756–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.06.018
Qin, Y., Mitchell, R., & Forgan, B. W. (2015). Characterizing the aerosol and surface reflectance over Australia using AATSR. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 53(11), 6163–6182. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2015.2433911
Schaaf, C., Gao, F., Strahler, A., Lucht, W., Li, X., & Tsang, T. et al. (2002). First operational BRDF, albedo nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sensing Of Environment, 83(1-2), 135-148. https://www.doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(02)00091-3
SZA. (2011). Retrieved May 2019, from http://sacs.aeronomie.be/info/sza.php
Zhu, Z., Wang, S., & Woodcock, C. (2015). Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sensing Of Environment, 159, 269-277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.12.014
Zhu, Z., & Woodcock, C. E. (2012). Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 118, 83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.10.028
Accuracy
For detailed information on accuracy and limitations, refer to the sub-products’ pages:
Quality assurance
For detailed information on quality assurance, refer to the sub-products’ pages:
The technical report containing the data summary for the Phase 1 DEA Surface Reflectance Validation is available.
Product ID
The Product ID is ga_ls5t_ard_3. This ID is used to load data from the Open Data Cube (ODC), for example dc.load(product="ga_ls5t_ard_3", ...)
Bands
Bands are distinct layers of data within a product that can be loaded using the Open Data Cube (on the DEA Sandbox or NCI) or DEA’s STAC API. Note that the Coordinate Reference System (CRS) of these bands is Multiple UTM zone CRSs.
Type |
Units |
Resolution |
No-data |
Aliases |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
nbart_blue |
int16 |
- |
30 |
-999 |
nbart_band01
blue
|
NBART surface reflectance for the blue spectral band. Wavelength: 0.45–0.52 µm. |
nbart_green |
int16 |
- |
30 |
-999 |
nbart_band02
green
|
NBART surface reflectance for the green spectral band. Wavelength: 0.52–0.60 µm. |
nbart_red |
int16 |
- |
30 |
-999 |
nbart_band03
red
|
NBART surface reflectance for the red spectral band. Wavelength: 0.63–0.69 µm. |
nbart_nir |
int16 |
- |
30 |
-999 |
nbart_band04
nir
nbart_common_nir
|
NBART surface reflectance for the Near Infrared (NIR) spectral band. Wavelength: 0.76–0.90 µm. |
nbart_swir_1 |
int16 |
- |
30 |
-999 |
nbart_band05
swir_1
nbart_common_swir_1
swir1
|
NBART surface reflectance for the Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) 1 spectral band. Wavelength: 1.55–1.75 µm. |
nbart_swir_2 |
int16 |
- |
30 |
-999 |
nbart_band07
swir_2
nbart_common_swir_2
swir2
|
NBART surface reflectance for the Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) 2 spectral band. Wavelength: 2.08–2.35 µm. |
oa_fmask |
uint8 |
Classification |
30 |
0 |
fmask
|
Fmask: A categorical classification layer produced using the automated Fmask (‘Function of mask’) algorithm, used to mask out unwanted observations in satellite imagery (e.g. cloud or shadow). Classification values: |
oa_nbart_contiguity |
uint8 |
Classification |
30 |
255 |
nbart_contiguity
|
NBART contiguity: A layer indicating whether each pixel is ‘spectrally contiguous’, meaning that it contains valid observations in every spectral band. Classification values: |
oa_azimuthal_exiting |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
azimuthal_exiting
|
Azimuthal exiting: The angle between true north and the exiting direction in the slope geometry. |
oa_azimuthal_incident |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
azimuthal_incident
|
Azimuthal incident: The angle between true north and the incident direction in the slope geometry. |
oa_combined_terrain_shadow |
uint8 |
Classification |
30 |
255 |
combined_terrain_shadow
|
Combined terrain shadow: Terrain shadow. Classification values: |
oa_exiting_angle |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
exiting_angle
|
Exiting angle: The angle between a ray reflected from a surface and the line perpendicular to the surface at the point of emergence. |
oa_incident_angle |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
incident_angle
|
Incident angle: The angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence. |
oa_relative_azimuth |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
relative_azimuth
|
Relative azimuth: The relative azimuth angle between the sun and view directions. |
oa_relative_slope |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
relative_slope
|
Relative slope: The relative azimuth angle between the incident and exiting directions in the slope geometry. |
oa_satellite_azimuth |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
satellite_azimuth
|
Satellite azimuth: The angle of the satellite’s position from true north; i.e. the angle between true north and a vertical circle passing through the satellite and the point being imaged on Earth. |
oa_satellite_view |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
satellite_view
|
Satellite view or satellite zenith: The angle between the zenith and the satellite. (The zenith is the point in the sky or celestial sphere directly above the point being imaged on Earth.) |
oa_solar_azimuth |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
solar_azimuth
|
Solar azimuth: The angle of the sun’s position from true north; i.e. the angle between true north and a vertical circle passing through the sun and the point being imaged on Earth. |
oa_solar_zenith |
float32 |
Degrees |
30 |
NaN |
solar_zenith
|
Solar zenith: The angle between the zenith and the centre of the sun’s disc. |
oa_time_delta |
float32 |
Seconds |
30 |
NaN |
time_delta
|
Timedelta: The time from satellite apogee (the point of orbit at which the satellite is furthest from the Earth). |
For all ‘nbart_’ bands, Surface Reflectance is scaled between 0 and 10,000.
Product information
This metadata provides general information about the product.
Product ID |
ga_ls5t_ard_3
|
Used to load data from the Open Data Cube. |
Short name |
DEA Surface Reflectance (Landsat 5 TM) |
The name that is commonly used to refer to the product. |
Technical name |
Geoscience Australia Landsat 5 TM Analysis Ready Data Collection 3 |
The full technical name that refers to the product and its specific provider, sensors, and collection. |
Version |
3.0.0 |
The version number of the product. See the History tab. |
Lineage type |
Baseline |
Baseline products are produced directly from satellite data. |
Spatial type |
Raster |
Raster data consists of a grid of pixels. |
Spatial resolution |
30 m |
The size of the pixels in the raster. |
Temporal coverage |
16 Aug 1986 to 17 Nov 2011 |
The time span for which data is available. |
Coordinate Reference System (CRS) |
Multiple UTM zone CRSs |
The method of mapping spatial data to the Earth’s surface. |
Update frequency |
Daily |
The expected frequency of data updates. Also called ‘Temporal resolution’. |
Update activity |
No further updates |
The activity status of data updates. |
Catalogue ID |
The Data and Publications catalogue (eCat) ID. |
|
Licence |
See the Credits tab. |
Product categorisation
This metadata describes how the product relates to other products.
Collection |
|
Tags |
geoscience_australia_landsat_collection_3, analysis_ready_data, satellite_images, earth_observation |
Access the data
DEA Maps |
Learn how to use DEA Maps. |
|
DEA Explorer |
Learn how to use the DEA Explorer. |
|
Data sources |
Learn how to access the data via AWS. |
|
Code examples |
Learn how to use the DEA Sandbox. |
Version history
Versions are numbered using the Semantic Versioning scheme (Major.Minor.Patch). Note that this list may include name changes and predecessor products.
v3.0.0 |
- |
Current version |
v2.0.0 |
of |
Frequently asked questions
Why doesn’t DEA make Landsat thermal bands available to users?
Landsat satellite sensors not only collect data in the short-wave spectrum but also collect data into the thermal infrared bands. The USGS makes this data available in the form of a surface temperature and emissivity product: Landsat Collection 2 Surface Temperature. It provides this separately to the surface reflectance products.
This USGS Surface Temperature product is a global product that uses global datasets to perform corrections on the data that are collected by the satellite sensors. The land surface temperature outputs are very sensitive to the atmospheric profile data that is used to perform the correction. For the global analysis, the NASA Modern Era Retrospective-Analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA) atmospheric data is used to provide values for height, air temperature, and humidity. While this dataset works well for a global correction, studies over Australia have shown that the correction can be improved when higher resolution datasets are considered (Li et al, 2015).
DEA’s ARD product provides high-quality data corrections for Australian conditions. At present, we do not produce a custom land surface temperature dataset for Australia, and so we have not included the thermal bands in our ARD package.
If you would like to use USGS Landsat thermal data directly, we provide a Jupyter notebook that shows you how to combine DEA ARD data with USGS thermal data.
Acknowledgments
This research was undertaken with the assistance of resources from the National Computational Infrastructure (NCI), which is supported by the Australian Government.
Landsat level 0 and level 1 data courtesy of the U.S. Geological Survey.
The authors would like to thank the following organisations:
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
Environment Canada
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO)
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) / Earth System Research Laboratories (ESRL) / Physical Sciences Laboratory (PSD)
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA)
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) / Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center
Spectral Sciences Inc.
License and copyright
© Commonwealth of Australia (Geoscience Australia).
Released under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence.